Understanding Animal Cell Structure: Animal Cell Coloring Sheet Pdf
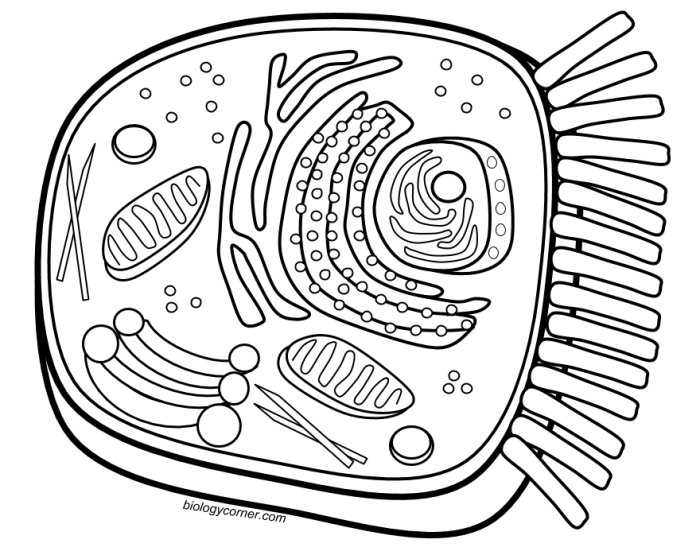
Animal cell coloring sheet pdf – The animal cell, a fundamental building block of animal life, is a marvel of intricate organization. Understanding its structure is key to grasping the complexities of biological processes. This section delves into the major components of an animal cell, highlighting their functions and contrasting them with plant cells. We will also explore the crucial role of the cell membrane.
Major Organelles and Their Functions, Animal cell coloring sheet pdf
Animal cells contain various organelles, each with a specific role in maintaining cellular function. These organelles work together in a coordinated manner to ensure the cell’s survival and proper functioning. The efficient collaboration of these structures is essential for the overall health and activity of the organism.
| Organelle | Function | Appearance in Coloring Sheet |
|---|---|---|
| Nucleus | Contains the cell’s genetic material (DNA) and controls cell activities. | A large, round structure, often darker than the surrounding cytoplasm. It might be shown with a distinct membrane. |
| Ribosomes | Synthesize proteins, essential for various cellular processes. | Small, numerous dots scattered throughout the cytoplasm and on the rough endoplasmic reticulum. They may be represented as small circles or specks. |
| Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER) | Network of membranes involved in protein and lipid synthesis and transport. Rough ER (with ribosomes) and smooth ER (without ribosomes) have different functions. | A network of interconnected tubes and sacs. Rough ER might appear bumpy due to the ribosomes attached to it, while smooth ER appears smoother. |
| Golgi Apparatus (Golgi Body) | Processes and packages proteins and lipids for transport within or outside the cell. | A stack of flattened sacs, often depicted as a series of layered pancakes. |
| Mitochondria | Powerhouse of the cell; responsible for cellular respiration, generating energy (ATP). | Rod-shaped or oval structures, often depicted with inner and outer membranes, possibly with internal cristae. |
| Lysosomes | Contain enzymes that break down waste materials and cellular debris. | Small, membrane-bound sacs, often depicted as smaller, darker circles than other organelles. |
| Vacuoles | Store water, nutrients, and waste products. Generally smaller and more numerous in animal cells compared to plant cells. | Small, membrane-bound sacs, often depicted as clear or lightly colored circles. |
| Cytoskeleton | Provides structural support and facilitates cell movement. | A network of protein fibers throughout the cytoplasm, often subtly represented by lines or shading. |
| Cell Membrane | Regulates the passage of substances into and out of the cell. | A thin outer boundary surrounding the entire cell, depicted as a continuous line. |
Differences Between Plant and Animal Cells
Plant and animal cells share some similarities but also exhibit key differences. These differences reflect the distinct needs and functions of these two cell types. A primary distinction lies in the presence of a cell wall and chloroplasts in plant cells.Plant cells possess a rigid cell wall made of cellulose, providing structural support and protection. They also contain chloroplasts, which are responsible for photosynthesis, enabling plants to produce their own food.
Animal cells lack both a cell wall and chloroplasts, relying on external sources for nutrients. Plant cells typically have a large central vacuole for water storage, whereas animal cells have smaller, more numerous vacuoles.
The Cell Membrane and Its Role
The cell membrane is a selectively permeable barrier that surrounds the cell, regulating the movement of substances in and out. It is composed primarily of a phospholipid bilayer, with embedded proteins that facilitate transport. This dynamic structure plays a critical role in maintaining cellular homeostasis by controlling the passage of nutrients, waste products, and signaling molecules. The cell membrane’s selective permeability ensures that the internal environment of the cell remains stable despite fluctuations in the external environment.
For example, it allows essential nutrients to enter the cell while preventing harmful substances from entering and crucial molecules from leaving.
Finding a good animal cell coloring sheet pdf can be helpful for educational purposes, especially when visualizing the intricate details of cell structures. For a broader exploration of animal forms, you might enjoy the delightful illustrations found in design originals creative coloring animals , offering a different creative outlet. Returning to the cellular level, detailed animal cell coloring sheets provide a valuable learning tool for students of all ages.
